Bolts & Nuts
Aluminum hub centric rings, why not plastic?
Aluminum hub centric rings for wheels, a small part that makes a big difference in drivability.
When you bolt on a set of nicer aftermarket alloy wheels or wheels from another car model, quite often the center bore of the wheel is either intentionally larger (so the manufacturer’s design fits as many cars as possible) or happens to be from a car with a larger hub size.
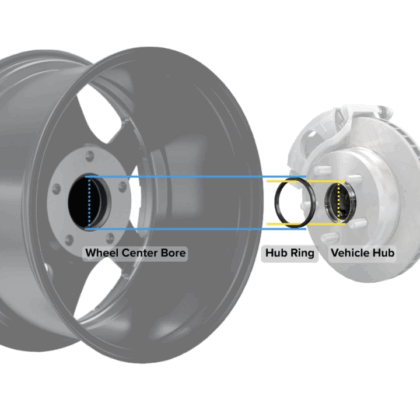
In that case you’ll need a center bore adapter ring, commonly called a hub ring or hub centric ring.
Why is a hub ring important?
The wheel must be perfectly centered on the hub, of course. Even the tiniest misalignment can naturally cause vibration or shaking at certain speeds.
Logic might say that the wheel centers itself when the bolts are tightened — and technically that’s partly true. The wheel center or ring itself does not carry the car’s weight, otherwise plastic rings would fail instantly. The clamping force actually comes from the bolts and the friction between the wheel and hub.
But in real life many drivers have noticed otherwise: wheels can mysteriously start vibrating if the centering ring is missing. So it’s much easier to just do it right from the start instead of troubleshooting later.
If the wheel center bore is larger than the hub:
-
the wheel will tighten into place with the bolts, but easily just slightly off-center
-
it can easily cause vibration at certain speeds
-
vibration puts stress on the wheel bearing and hub (and the driver)
-
driving comfort suffers
👉 A hub ring ensures the wheel sits perfectly centered on the hub even before tightening, exactly as it should.
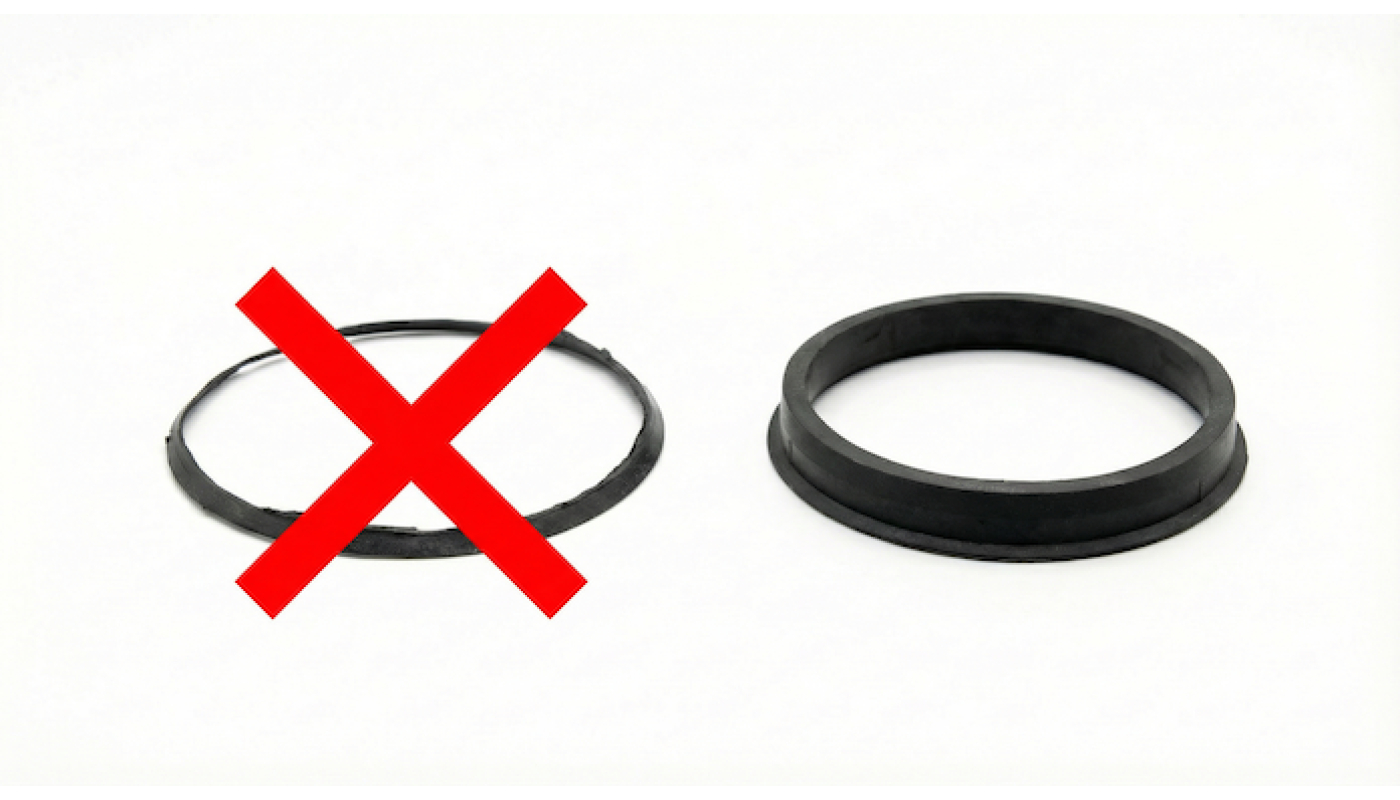
Why are aluminum hub rings better than plastic ones?
First of all, aluminum rings usually aren’t much more expensive than plastic ones as you’ll see from our selection below — prices are for sets of 4. Secondly, as common sense suggests, aluminum is a more rigid material and when precision-machined it fits your alloy wheel as accurately as if the wheels had been factory-made with the exact correct bore.
All aluminum wheels sold by Futurez include vehicle-specific plastic hub rings at no extra cost.
Plastic rings work perfectly fine for normal driving, but aluminum rings offer clear advantages depending on use.
-
withstand heat near the brakes, plastic ones can lose shape during track driving
-
do not deform under heavy load
-
maintain precise tolerances for years, tire change after tire change
-
easier to install and remove
-
can melt under hard driving, the hub heats up during braking
-
may crack over time or if the wheel is installed carelessly
-
can get stuck inside the wheel
Popular hub ring sizes
Aftermarket wheels are often manufactured with a 73.1 or 74.1 center bore so they can fit as many vehicles as possible when used with the correct adapter ring. This is also the most practical approach for manufacturers from a logistics standpoint.
In addition, there are certain cases where even within the same brand the hub bore size has changed between model years.
A couple of examples:
- BMW 74.1 and 72.6 mm hubs. Older BMW models used the larger bore, which won’t center properly on newer 72.6 hubs even though the bolt pattern and other specs may match. Wheels originally made for older BMWs can be fitted to newer ones using a 74.1–72.6 mm hub ring.
- Audi / VW 66.6 and 57.1 hubs. VAG cars were historically known for 57.1 mm hubs, but around 2008–2010 many models switched to a 66.6 center bore. So if you install newer VAG wheels onto an older vehicle, you may need 66.6–57.1 mm hub rings.
- Typical aftermarket wheels are often 73.1 bore, so you may need a 73.1 → your vehicle hub adapter.
TIP: You can easily check your car’s hub size for example from Wheel-Size.com.
Below are some common sizes:
| Diameter | Manufacturers | Example |
|---|---|---|
| 74.1 mm | BMW | Older BMW models |
| 72.6 mm | BMW | Newer BMW (E/F/G chassis) |
| 71.6 mm | Mercedes-Benz | Many Mercedes models 1990→ |
| 70.1 mm | MINI | MINI R-series + F-series |
| 66.6 mm | VAG | Newer VAG brands |
| 65.1 mm | Toyota | Toyota, Lexus, Subaru |
| 64.1 mm | Honda | Honda, Acura |
| 63.4 mm | Nissan | Nissan, Infiniti |
| 60.1 mm | Mazda, Toyota | Many Mazda models and Toyota |
| 54.1 mm | Hyundai | Hyundai, Kia |